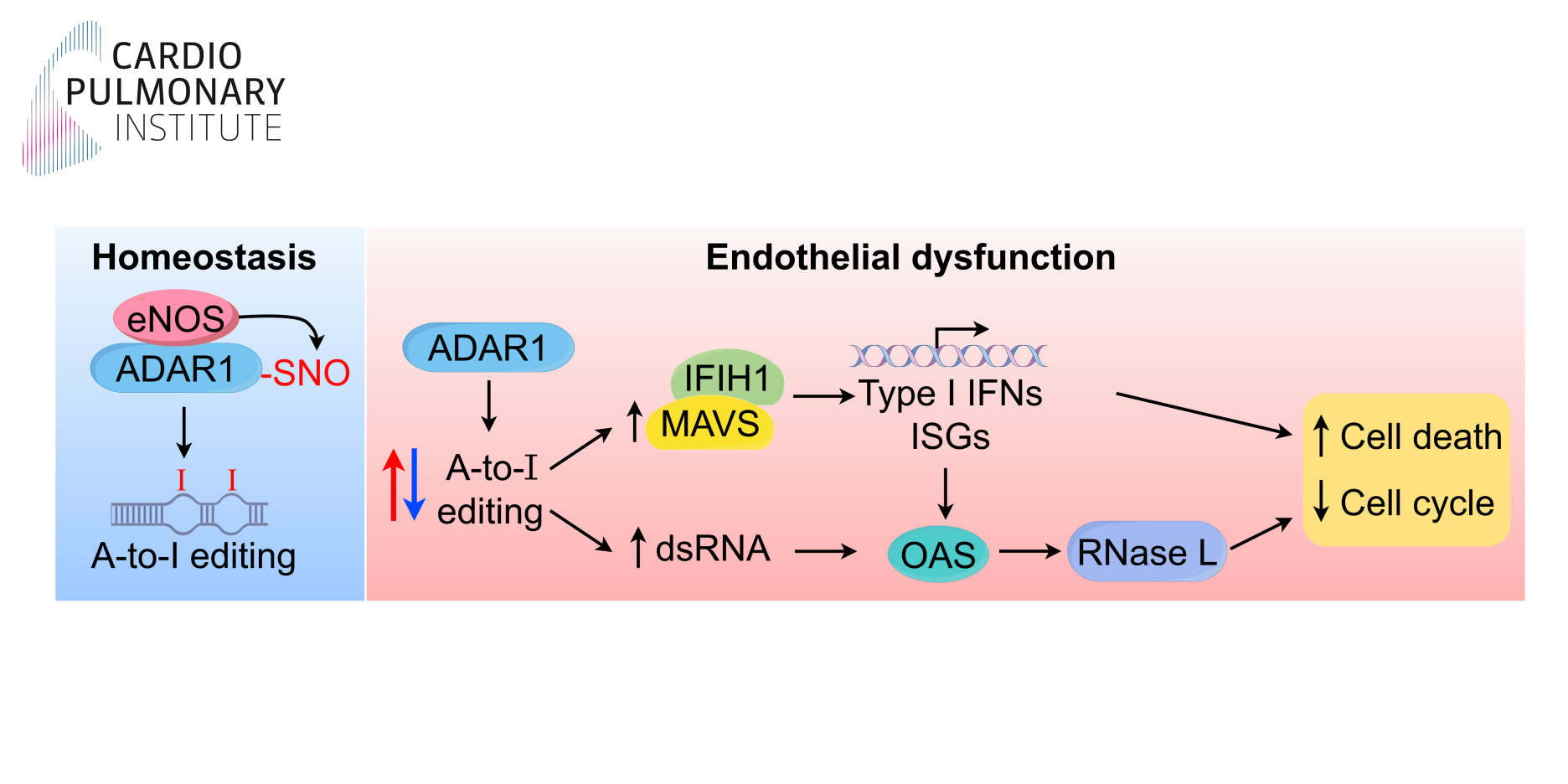
A research team at Goethe University Frankfurt has identified a previously unrecognized type I interferonopathy, driven by reduced nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, as a contributor to the development of atherosclerosis.
NO generated by the endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) regulates vascular tone and endothelial homeostasis and plays a key role in limiting vascular inflammation. While eNOS is predominantly localized at the plasma membrane and the Golgi apparatus, a fraction of the enzyme is also present in the endothelial cell nucleus. Using a combination of biochemical approaches and mass spectrometry-based proteomics, the team demonstrated that nuclear eNOS interacts with multiple nuclear proteins, including the double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase ADAR1, which mediates adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing of endogenous double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). In endothelial cells, ADAR1 is S-nitrosated and eNOS loss-of-function in vitro, as well as endothelial dysfunction in mice and in patients with atherosclerosis, is associated with reduced ADAR1 S-nitrosation, accumulation of dsRNA, and activation of a type I interferon response.
Together, these findings reveal a novel mechanism linking nuclear eNOS-derived NO to ADAR1 activity in the maintenance of vascular homeostasis and suggest that therapeutic strategies targeting type I interferon signaling should be reconsidered in the context of cardiovascular disease.
Find the full article here: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.125.074889?af=R
You need to load content from hCaptcha to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from Turnstile to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information